Jan 28, 2026
In-House Warranty Management vs Shopify Apps
In-House Warranty Management vs Shopify Apps
In-House Warranty Management vs Shopify Apps



A Complete, No-Fluff Warranty Management Guide for Shopify Store Owners
If you sell physical products, warranties are not optional. And warranties always sound simple when you are planning them.
You sell a product.
You promise to fix or replace it if something goes wrong.
You move on.
That simplicity usually lasts until the first real warranty claim lands in your inbox. Then another one follows. Then a support agent asks where warranty data is stored. Someone checks Shopify orders. Someone else checks emails. Customers follow up asking for updates. Suddenly, something that was meant to build trust starts creating friction inside your business.
This is where most Shopify brands hit a crossroads.
Do you build and manage your own warranty system internally, fully in-house, with your own processes, tools, and workflows? Or do you use a Shopify warranty management app that handles tracking, claims, communication, and automation for you?
This guide walks through that decision completely, not from a theoretical angle, but from the perspective of real Shopify stores, real operational challenges, and real tradeoffs. By the end, you should have enough clarity to confidently choose the path that actually fits your business instead of guessing or copying what others are doing.
What Is In-House Warranty Management?

In-house warranty management means you design, build, and operate your own warranty system internally. This does not just mean replying to warranty emails. It means owning the entire lifecycle of warranty coverage, from defining policies to tracking eligibility, validating claims, resolving issues, and maintaining records.
For many Shopify brands, in-house starts unintentionally. A customer emails support saying their product stopped working. The support agent checks the order date in Shopify, confirms it is within warranty, and sends a replacement. That feels simple, and for low volume, it works. Over time, this informal process evolves into something more structured. Spreadsheets appear. Internal guidelines are written. Maybe a form is added to the website. Eventually, some brands even consider building a custom internal tool or portal to manage warranties more systematically.
True in-house warranty management is not just manual handling. It often includes building or stitching together systems like internal dashboards, databases, custom forms, automation through tools like Zapier, and internal workflows across support, operations, and fulfillment. The brand owns the logic, the data, the rules, and the responsibility.
The appeal of in-house is control. You decide how strict or flexible your policies are. You decide how claims are evaluated. You decide what data you collect and how it is stored. You also keep full ownership of the customer relationship and any revenue tied to warranties or extended protection plans.
However, that control comes with complexity. Every rule you create must be enforced manually or through systems you build. Every edge case must be handled by your team. As volume grows, the system must scale or it will break under its own weight.
What Is a Shopify Warranty Management App?

A Shopify warranty management app is software designed specifically to help brands organize, track, and manage warranties inside their Shopify ecosystem. Instead of building your own system from scratch, the app provides a structured framework that connects customers, warranty data, and internal workflows in one place.
Using a Shopify app does not mean outsourcing your warranty responsibility. The brand still owns the warranty policy, makes the final decisions, and fulfills claims. The difference is that the infrastructure is already built for you.
An end-to-end warranty management app like Dyrect is designed around two clear experiences, one for customers and one for brands.
From the customer’s side
Customers interact with the warranty process in a simple and intentional way. Warranties are not created automatically in the background. Instead, customers actively register their product, which makes the process clear and transparent.
Typical customer actions include:
Registering their product using a simple form after purchase
Scanning a QR code included with the product to complete warranty registration
Receiving confirmation that their warranty is successfully registered
Submitting a warranty claim through a guided claim form when needed
This approach ensures that warranty records are tied to real customer intent and real products, reducing confusion and future disputes.
From the brand’s side
For brands, the app acts as a central source of truth for everything related to warranties. All registrations, claims, and supporting details live in one structured system rather than being scattered across emails, notes, and Shopify orders.
Brands can:
View all registered warranties in one place
See warranty start and end dates clearly
Track claim requests with full context
Review claim history without digging through past conversations
Instead of reacting to warranty issues manually, teams work from a clear and organized dashboard.
How In-House Warranty Management Works (Process)
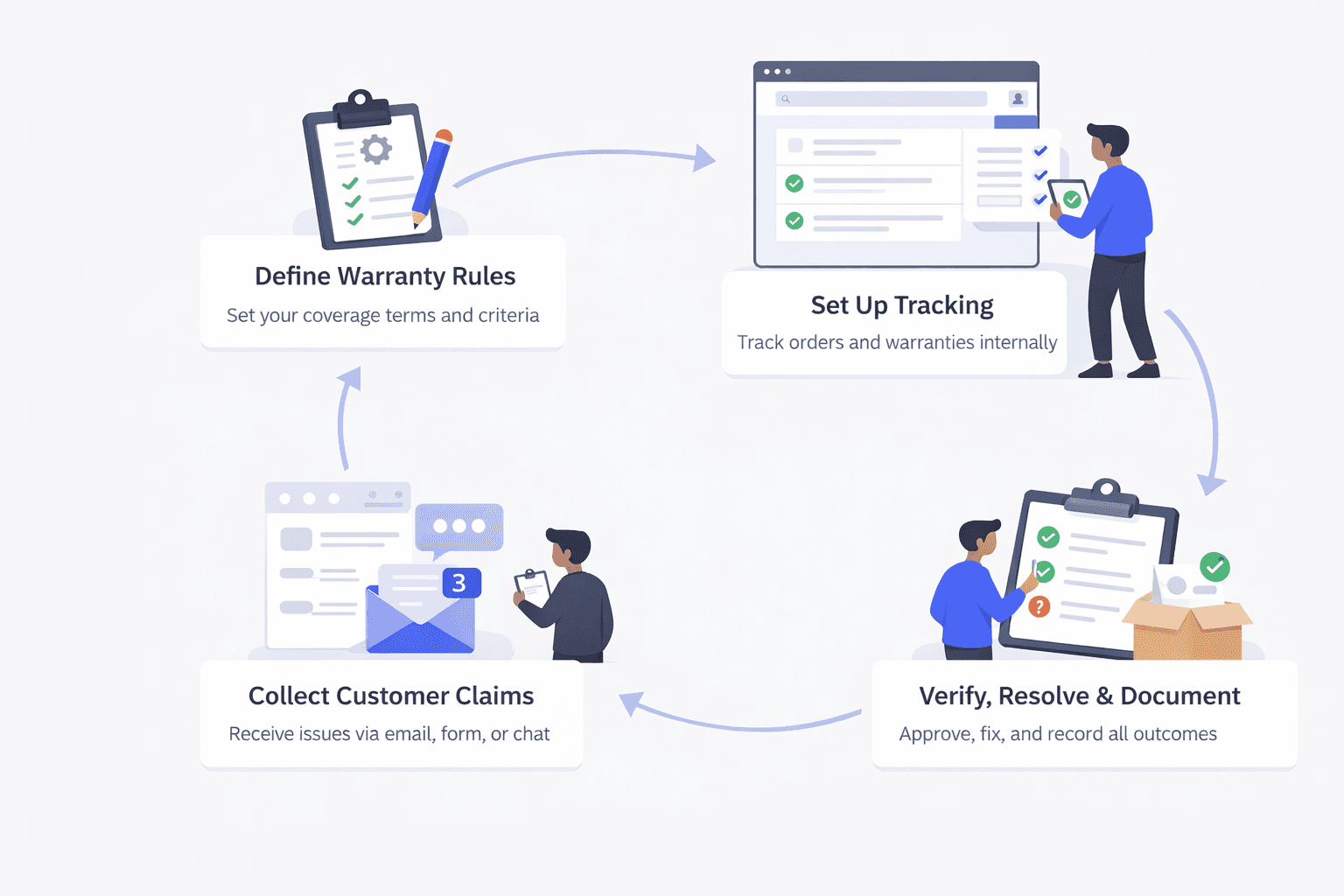
In-house warranty management means your team runs the entire warranty flow using your own process. That can be fully manual, or supported by an internal system your team builds and maintains. The steps usually look like this.
Define the warranty rules
You decide what is covered, for how long, what proof is required, and how claims are handled. These rules live on your policy page and in internal notes so the team applies them consistently.
Set up tracking for eligibility
In a manual setup, teams rely on Shopify order history, email threads, and sometimes spreadsheets to track purchase dates and warranty periods. In a more advanced setup, the team builds an internal tool or database that stores warranty records, coverage dates, and product details.
Collect claim requests from customers
Customers usually reach out through email, contact forms, or support chat. They share the order number, issue details, photos, and any extra information needed. If details are missing, the support team follows up to gather them.
Verify coverage and validate the claim
Your team checks whether the product is within the warranty window and whether the issue fits your policy. In a manual process, this is done by looking up the order and reviewing the conversation. In an internal system, eligibility checks may be faster, but still depend on correct data and consistent rules.
Resolve and document the outcome
If approved, you arrange a repair, replacement, part shipment, or refund. Then the team records what happened, either in Shopify notes, a spreadsheet, a ticketing tool, or your internal system, so future claims can be handled with context.
How Warranty Management Apps on Shopify Work (Process)
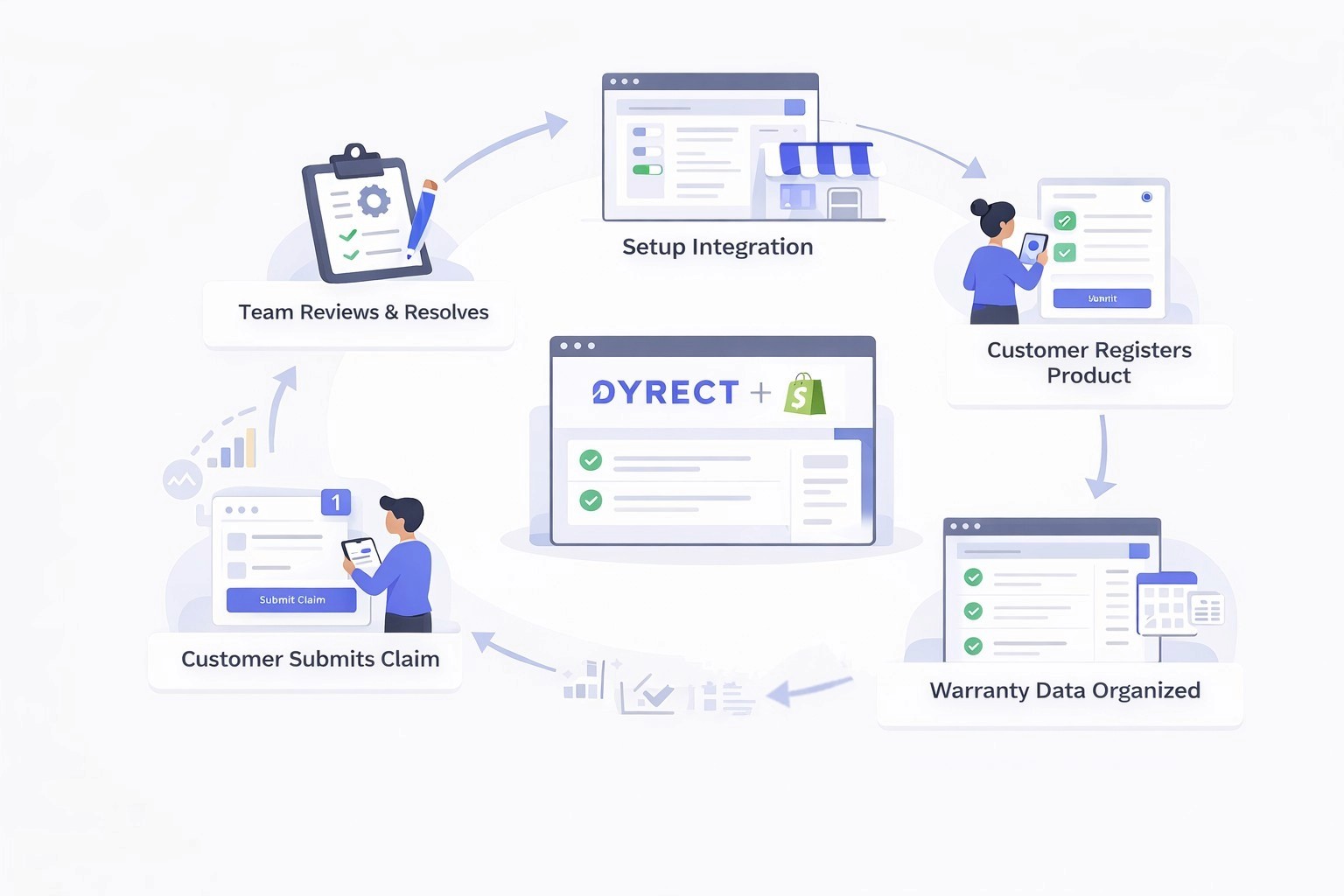
Now let’s look at how the same warranty journey works when using a warranty management app on Shopify such as Dyrect.
1) Brand setup and integration
The brand installs the app and adds a warranty registration option to the store. This usually looks like an embedded warranty form on a page, or a QR code link that ships with the product so customers can register after delivery. If the brand previously handled warranties manually or built an internal system, they map their existing rules (warranty duration, covered products, claim conditions) into the app settings so the process stays consistent.
2) Customer registers their products for warranty
After purchase, the customer registers their product using the form or QR code. They typically share basic details like name, email, order info, and product details. This step creates a clear record of coverage, which reduces confusion later when a claim is filed. If the brand wants, they can still keep their internal process in parallel, but the app becomes the main source of truth.
3) Warranty data gets organized in one place
Instead of tracking details across email threads, spreadsheets, or a custom database, the app stores registrations in a structured list inside Shopify. Teams can quickly check who registered, what they registered, and when coverage started.
4) Customer submits a claim through a guided flow
When something goes wrong, the customer files a claim using the same platform in just a few seconds by mentioning the issues they are facing.
5) Team reviews, decides, and closes the loop
The team reviews the claim, confirms eligibility based on the stored registration and rules, and then approves, rejects, or requests more information. Throughout the process, they can update customers on the status of their request. Once resolved, they mark the outcome and keep a consistent claim history for future reference.
This information feeds back into better product decisions, clearer policies, and improved customer experience.
In-House vs Shopify App: Key Differences
Choosing between in-house warranty management and a warranty management app on Shopify App Store is not about right or wrong. It is about understanding how each option behaves over time as your business grows. What feels simple today may become difficult later, and what feels like an extra step now may save effort in the future.
Below is a clear breakdown that looks at short-term and long-term impact, effort, cost, and operational clarity without assuming one approach automatically wins.
High-level comparison
Aspect to consider | In-House Warranty Management | Shopify Warranty Management App |
Short-term setup | Usually faster to start since teams use existing tools like email and spreadsheets | Requires initial setup but comes with a predefined structure |
Long-term maintenance | May increase as order volume and claims grow | Stays relatively stable even as volume increases |
Cost visibility | No fixed software fee, but time and manual work may add up | Clear monthly cost, with effort often reduced |
Team effort | Manual checks, follow-ups, and record keeping | Guided workflows reduce repetitive work |
Customer experience | Depends heavily on response speed and internal processes | More consistent due to structured forms and tracking |
Data clarity | Information may be spread across tools | Data stays in one organized system |
Scalability | May require more people or internal tools over time | Designed to handle growth without major changes |
Pros and Cons of Each Approach
Every warranty setup comes with trade-offs. What matters is understanding where each approach helps and where it may start creating friction, especially as your business grows.
In-House Warranty Management
Pros
Gives full control over warranty rules and how exceptions are handled
Allows flexible, human-led decisions on a case-by-case basis
Can work well at very low claim volumes
Avoids recurring software subscription costs
Cons
Manual effort may increase as orders and claims grow
Warranty data can become scattered across emails and tools
Response quality may vary depending on team workload
Building a custom internal system can require development time, ongoing maintenance, and technical resources, which may increase long-term costs
Warranty Management App
Pros
Provides a structured way to collect warranty registrations and claims
Keeps warranty data organized in one place for easier tracking
Helps maintain a more consistent customer experience
Effort per claim often stays stable even as volume increases
Cons
Requires initial setup and team familiarization
Introduces a recurring software cost
May feel more structured than needed for very low claim volumes
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Warranty Management Strategy for Your Shopify Store
In-house warranty management can make sense for very small teams or early-stage brands where claim volume is low and processes are simple. It offers flexibility and control, but effort, coordination, and internal costs may increase as the business grows or as warranties become more frequent.
A warranty management app like Dyrect becomes a stronger option when consistency, clarity, and scalability matter. It provides a structured way to manage registrations and claims without building your own system. For growing brands, this often makes warranties easier to manage and more reliable for both teams and customers.
A Complete, No-Fluff Warranty Management Guide for Shopify Store Owners
If you sell physical products, warranties are not optional. And warranties always sound simple when you are planning them.
You sell a product.
You promise to fix or replace it if something goes wrong.
You move on.
That simplicity usually lasts until the first real warranty claim lands in your inbox. Then another one follows. Then a support agent asks where warranty data is stored. Someone checks Shopify orders. Someone else checks emails. Customers follow up asking for updates. Suddenly, something that was meant to build trust starts creating friction inside your business.
This is where most Shopify brands hit a crossroads.
Do you build and manage your own warranty system internally, fully in-house, with your own processes, tools, and workflows? Or do you use a Shopify warranty management app that handles tracking, claims, communication, and automation for you?
This guide walks through that decision completely, not from a theoretical angle, but from the perspective of real Shopify stores, real operational challenges, and real tradeoffs. By the end, you should have enough clarity to confidently choose the path that actually fits your business instead of guessing or copying what others are doing.
What Is In-House Warranty Management?

In-house warranty management means you design, build, and operate your own warranty system internally. This does not just mean replying to warranty emails. It means owning the entire lifecycle of warranty coverage, from defining policies to tracking eligibility, validating claims, resolving issues, and maintaining records.
For many Shopify brands, in-house starts unintentionally. A customer emails support saying their product stopped working. The support agent checks the order date in Shopify, confirms it is within warranty, and sends a replacement. That feels simple, and for low volume, it works. Over time, this informal process evolves into something more structured. Spreadsheets appear. Internal guidelines are written. Maybe a form is added to the website. Eventually, some brands even consider building a custom internal tool or portal to manage warranties more systematically.
True in-house warranty management is not just manual handling. It often includes building or stitching together systems like internal dashboards, databases, custom forms, automation through tools like Zapier, and internal workflows across support, operations, and fulfillment. The brand owns the logic, the data, the rules, and the responsibility.
The appeal of in-house is control. You decide how strict or flexible your policies are. You decide how claims are evaluated. You decide what data you collect and how it is stored. You also keep full ownership of the customer relationship and any revenue tied to warranties or extended protection plans.
However, that control comes with complexity. Every rule you create must be enforced manually or through systems you build. Every edge case must be handled by your team. As volume grows, the system must scale or it will break under its own weight.
What Is a Shopify Warranty Management App?

A Shopify warranty management app is software designed specifically to help brands organize, track, and manage warranties inside their Shopify ecosystem. Instead of building your own system from scratch, the app provides a structured framework that connects customers, warranty data, and internal workflows in one place.
Using a Shopify app does not mean outsourcing your warranty responsibility. The brand still owns the warranty policy, makes the final decisions, and fulfills claims. The difference is that the infrastructure is already built for you.
An end-to-end warranty management app like Dyrect is designed around two clear experiences, one for customers and one for brands.
From the customer’s side
Customers interact with the warranty process in a simple and intentional way. Warranties are not created automatically in the background. Instead, customers actively register their product, which makes the process clear and transparent.
Typical customer actions include:
Registering their product using a simple form after purchase
Scanning a QR code included with the product to complete warranty registration
Receiving confirmation that their warranty is successfully registered
Submitting a warranty claim through a guided claim form when needed
This approach ensures that warranty records are tied to real customer intent and real products, reducing confusion and future disputes.
From the brand’s side
For brands, the app acts as a central source of truth for everything related to warranties. All registrations, claims, and supporting details live in one structured system rather than being scattered across emails, notes, and Shopify orders.
Brands can:
View all registered warranties in one place
See warranty start and end dates clearly
Track claim requests with full context
Review claim history without digging through past conversations
Instead of reacting to warranty issues manually, teams work from a clear and organized dashboard.
How In-House Warranty Management Works (Process)

In-house warranty management means your team runs the entire warranty flow using your own process. That can be fully manual, or supported by an internal system your team builds and maintains. The steps usually look like this.
Define the warranty rules
You decide what is covered, for how long, what proof is required, and how claims are handled. These rules live on your policy page and in internal notes so the team applies them consistently.
Set up tracking for eligibility
In a manual setup, teams rely on Shopify order history, email threads, and sometimes spreadsheets to track purchase dates and warranty periods. In a more advanced setup, the team builds an internal tool or database that stores warranty records, coverage dates, and product details.
Collect claim requests from customers
Customers usually reach out through email, contact forms, or support chat. They share the order number, issue details, photos, and any extra information needed. If details are missing, the support team follows up to gather them.
Verify coverage and validate the claim
Your team checks whether the product is within the warranty window and whether the issue fits your policy. In a manual process, this is done by looking up the order and reviewing the conversation. In an internal system, eligibility checks may be faster, but still depend on correct data and consistent rules.
Resolve and document the outcome
If approved, you arrange a repair, replacement, part shipment, or refund. Then the team records what happened, either in Shopify notes, a spreadsheet, a ticketing tool, or your internal system, so future claims can be handled with context.
How Warranty Management Apps on Shopify Work (Process)

Now let’s look at how the same warranty journey works when using a warranty management app on Shopify such as Dyrect.
1) Brand setup and integration
The brand installs the app and adds a warranty registration option to the store. This usually looks like an embedded warranty form on a page, or a QR code link that ships with the product so customers can register after delivery. If the brand previously handled warranties manually or built an internal system, they map their existing rules (warranty duration, covered products, claim conditions) into the app settings so the process stays consistent.
2) Customer registers their products for warranty
After purchase, the customer registers their product using the form or QR code. They typically share basic details like name, email, order info, and product details. This step creates a clear record of coverage, which reduces confusion later when a claim is filed. If the brand wants, they can still keep their internal process in parallel, but the app becomes the main source of truth.
3) Warranty data gets organized in one place
Instead of tracking details across email threads, spreadsheets, or a custom database, the app stores registrations in a structured list inside Shopify. Teams can quickly check who registered, what they registered, and when coverage started.
4) Customer submits a claim through a guided flow
When something goes wrong, the customer files a claim using the same platform in just a few seconds by mentioning the issues they are facing.
5) Team reviews, decides, and closes the loop
The team reviews the claim, confirms eligibility based on the stored registration and rules, and then approves, rejects, or requests more information. Throughout the process, they can update customers on the status of their request. Once resolved, they mark the outcome and keep a consistent claim history for future reference.
This information feeds back into better product decisions, clearer policies, and improved customer experience.
In-House vs Shopify App: Key Differences

Choosing between in-house warranty management and a warranty management app on Shopify App Store is not about right or wrong. It is about understanding how each option behaves over time as your business grows. What feels simple today may become difficult later, and what feels like an extra step now may save effort in the future.
Below is a clear breakdown that looks at short-term and long-term impact, effort, cost, and operational clarity without assuming one approach automatically wins.
High-level comparison
Aspect to consider | In-House Warranty Management | Shopify Warranty Management App |
Short-term setup | Usually faster to start since teams use existing tools like email and spreadsheets | Requires initial setup but comes with a predefined structure |
Long-term maintenance | May increase as order volume and claims grow | Stays relatively stable even as volume increases |
Cost visibility | No fixed software fee, but time and manual work may add up | Clear monthly cost, with effort often reduced |
Team effort | Manual checks, follow-ups, and record keeping | Guided workflows reduce repetitive work |
Customer experience | Depends heavily on response speed and internal processes | More consistent due to structured forms and tracking |
Data clarity | Information may be spread across tools | Data stays in one organized system |
Scalability | May require more people or internal tools over time | Designed to handle growth without major changes |
Pros and Cons of Each Approach

Every warranty setup comes with trade-offs. What matters is understanding where each approach helps and where it may start creating friction, especially as your business grows.
In-House Warranty Management
Pros
Gives full control over warranty rules and how exceptions are handled
Allows flexible, human-led decisions on a case-by-case basis
Can work well at very low claim volumes
Avoids recurring software subscription costs
Cons
Manual effort may increase as orders and claims grow
Warranty data can become scattered across emails and tools
Response quality may vary depending on team workload
Building a custom internal system can require development time, ongoing maintenance, and technical resources, which may increase long-term costs
Warranty Management App
Pros
Provides a structured way to collect warranty registrations and claims
Keeps warranty data organized in one place for easier tracking
Helps maintain a more consistent customer experience
Effort per claim often stays stable even as volume increases
Cons
Requires initial setup and team familiarization
Introduces a recurring software cost
May feel more structured than needed for very low claim volumes
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Warranty Management Strategy for Your Shopify Store
In-house warranty management can make sense for very small teams or early-stage brands where claim volume is low and processes are simple. It offers flexibility and control, but effort, coordination, and internal costs may increase as the business grows or as warranties become more frequent.
A warranty management app like Dyrect becomes a stronger option when consistency, clarity, and scalability matter. It provides a structured way to manage registrations and claims without building your own system. For growing brands, this often makes warranties easier to manage and more reliable for both teams and customers.
A Complete, No-Fluff Warranty Management Guide for Shopify Store Owners
If you sell physical products, warranties are not optional. And warranties always sound simple when you are planning them.
You sell a product.
You promise to fix or replace it if something goes wrong.
You move on.
That simplicity usually lasts until the first real warranty claim lands in your inbox. Then another one follows. Then a support agent asks where warranty data is stored. Someone checks Shopify orders. Someone else checks emails. Customers follow up asking for updates. Suddenly, something that was meant to build trust starts creating friction inside your business.
This is where most Shopify brands hit a crossroads.
Do you build and manage your own warranty system internally, fully in-house, with your own processes, tools, and workflows? Or do you use a Shopify warranty management app that handles tracking, claims, communication, and automation for you?
This guide walks through that decision completely, not from a theoretical angle, but from the perspective of real Shopify stores, real operational challenges, and real tradeoffs. By the end, you should have enough clarity to confidently choose the path that actually fits your business instead of guessing or copying what others are doing.
What Is In-House Warranty Management?

In-house warranty management means you design, build, and operate your own warranty system internally. This does not just mean replying to warranty emails. It means owning the entire lifecycle of warranty coverage, from defining policies to tracking eligibility, validating claims, resolving issues, and maintaining records.
For many Shopify brands, in-house starts unintentionally. A customer emails support saying their product stopped working. The support agent checks the order date in Shopify, confirms it is within warranty, and sends a replacement. That feels simple, and for low volume, it works. Over time, this informal process evolves into something more structured. Spreadsheets appear. Internal guidelines are written. Maybe a form is added to the website. Eventually, some brands even consider building a custom internal tool or portal to manage warranties more systematically.
True in-house warranty management is not just manual handling. It often includes building or stitching together systems like internal dashboards, databases, custom forms, automation through tools like Zapier, and internal workflows across support, operations, and fulfillment. The brand owns the logic, the data, the rules, and the responsibility.
The appeal of in-house is control. You decide how strict or flexible your policies are. You decide how claims are evaluated. You decide what data you collect and how it is stored. You also keep full ownership of the customer relationship and any revenue tied to warranties or extended protection plans.
However, that control comes with complexity. Every rule you create must be enforced manually or through systems you build. Every edge case must be handled by your team. As volume grows, the system must scale or it will break under its own weight.
What Is a Shopify Warranty Management App?

A Shopify warranty management app is software designed specifically to help brands organize, track, and manage warranties inside their Shopify ecosystem. Instead of building your own system from scratch, the app provides a structured framework that connects customers, warranty data, and internal workflows in one place.
Using a Shopify app does not mean outsourcing your warranty responsibility. The brand still owns the warranty policy, makes the final decisions, and fulfills claims. The difference is that the infrastructure is already built for you.
An end-to-end warranty management app like Dyrect is designed around two clear experiences, one for customers and one for brands.
From the customer’s side
Customers interact with the warranty process in a simple and intentional way. Warranties are not created automatically in the background. Instead, customers actively register their product, which makes the process clear and transparent.
Typical customer actions include:
Registering their product using a simple form after purchase
Scanning a QR code included with the product to complete warranty registration
Receiving confirmation that their warranty is successfully registered
Submitting a warranty claim through a guided claim form when needed
This approach ensures that warranty records are tied to real customer intent and real products, reducing confusion and future disputes.
From the brand’s side
For brands, the app acts as a central source of truth for everything related to warranties. All registrations, claims, and supporting details live in one structured system rather than being scattered across emails, notes, and Shopify orders.
Brands can:
View all registered warranties in one place
See warranty start and end dates clearly
Track claim requests with full context
Review claim history without digging through past conversations
Instead of reacting to warranty issues manually, teams work from a clear and organized dashboard.
How In-House Warranty Management Works (Process)

In-house warranty management means your team runs the entire warranty flow using your own process. That can be fully manual, or supported by an internal system your team builds and maintains. The steps usually look like this.
Define the warranty rules
You decide what is covered, for how long, what proof is required, and how claims are handled. These rules live on your policy page and in internal notes so the team applies them consistently.
Set up tracking for eligibility
In a manual setup, teams rely on Shopify order history, email threads, and sometimes spreadsheets to track purchase dates and warranty periods. In a more advanced setup, the team builds an internal tool or database that stores warranty records, coverage dates, and product details.
Collect claim requests from customers
Customers usually reach out through email, contact forms, or support chat. They share the order number, issue details, photos, and any extra information needed. If details are missing, the support team follows up to gather them.
Verify coverage and validate the claim
Your team checks whether the product is within the warranty window and whether the issue fits your policy. In a manual process, this is done by looking up the order and reviewing the conversation. In an internal system, eligibility checks may be faster, but still depend on correct data and consistent rules.
Resolve and document the outcome
If approved, you arrange a repair, replacement, part shipment, or refund. Then the team records what happened, either in Shopify notes, a spreadsheet, a ticketing tool, or your internal system, so future claims can be handled with context.
How Warranty Management Apps on Shopify Work (Process)

Now let’s look at how the same warranty journey works when using a warranty management app on Shopify such as Dyrect.
1) Brand setup and integration
The brand installs the app and adds a warranty registration option to the store. This usually looks like an embedded warranty form on a page, or a QR code link that ships with the product so customers can register after delivery. If the brand previously handled warranties manually or built an internal system, they map their existing rules (warranty duration, covered products, claim conditions) into the app settings so the process stays consistent.
2) Customer registers their products for warranty
After purchase, the customer registers their product using the form or QR code. They typically share basic details like name, email, order info, and product details. This step creates a clear record of coverage, which reduces confusion later when a claim is filed. If the brand wants, they can still keep their internal process in parallel, but the app becomes the main source of truth.
3) Warranty data gets organized in one place
Instead of tracking details across email threads, spreadsheets, or a custom database, the app stores registrations in a structured list inside Shopify. Teams can quickly check who registered, what they registered, and when coverage started.
4) Customer submits a claim through a guided flow
When something goes wrong, the customer files a claim using the same platform in just a few seconds by mentioning the issues they are facing.
5) Team reviews, decides, and closes the loop
The team reviews the claim, confirms eligibility based on the stored registration and rules, and then approves, rejects, or requests more information. Throughout the process, they can update customers on the status of their request. Once resolved, they mark the outcome and keep a consistent claim history for future reference.
This information feeds back into better product decisions, clearer policies, and improved customer experience.
In-House vs Shopify App: Key Differences

Choosing between in-house warranty management and a warranty management app on Shopify App Store is not about right or wrong. It is about understanding how each option behaves over time as your business grows. What feels simple today may become difficult later, and what feels like an extra step now may save effort in the future.
Below is a clear breakdown that looks at short-term and long-term impact, effort, cost, and operational clarity without assuming one approach automatically wins.
High-level comparison
Aspect to consider | In-House Warranty Management | Shopify Warranty Management App |
Short-term setup | Usually faster to start since teams use existing tools like email and spreadsheets | Requires initial setup but comes with a predefined structure |
Long-term maintenance | May increase as order volume and claims grow | Stays relatively stable even as volume increases |
Cost visibility | No fixed software fee, but time and manual work may add up | Clear monthly cost, with effort often reduced |
Team effort | Manual checks, follow-ups, and record keeping | Guided workflows reduce repetitive work |
Customer experience | Depends heavily on response speed and internal processes | More consistent due to structured forms and tracking |
Data clarity | Information may be spread across tools | Data stays in one organized system |
Scalability | May require more people or internal tools over time | Designed to handle growth without major changes |
Pros and Cons of Each Approach

Every warranty setup comes with trade-offs. What matters is understanding where each approach helps and where it may start creating friction, especially as your business grows.
In-House Warranty Management
Pros
Gives full control over warranty rules and how exceptions are handled
Allows flexible, human-led decisions on a case-by-case basis
Can work well at very low claim volumes
Avoids recurring software subscription costs
Cons
Manual effort may increase as orders and claims grow
Warranty data can become scattered across emails and tools
Response quality may vary depending on team workload
Building a custom internal system can require development time, ongoing maintenance, and technical resources, which may increase long-term costs
Warranty Management App
Pros
Provides a structured way to collect warranty registrations and claims
Keeps warranty data organized in one place for easier tracking
Helps maintain a more consistent customer experience
Effort per claim often stays stable even as volume increases
Cons
Requires initial setup and team familiarization
Introduces a recurring software cost
May feel more structured than needed for very low claim volumes
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Warranty Management Strategy for Your Shopify Store
In-house warranty management can make sense for very small teams or early-stage brands where claim volume is low and processes are simple. It offers flexibility and control, but effort, coordination, and internal costs may increase as the business grows or as warranties become more frequent.
A warranty management app like Dyrect becomes a stronger option when consistency, clarity, and scalability matter. It provides a structured way to manage registrations and claims without building your own system. For growing brands, this often makes warranties easier to manage and more reliable for both teams and customers.
Read more articles
Revize your Shopify store, and lead with
customer experience
© Copyright 2024, All Rights Reserved
Revize your Shopify store, and lead with
customer experience
© Copyright 2024, All Rights Reserved
Revize your Shopify store, and lead with
customer experience
© Copyright 2024, All Rights Reserved
Revize your Shopify store, and lead with
customer experience
© Copyright 2024, All Rights Reserved
Revize your Shopify store, and lead with
customer experience
© Copyright 2024, All Rights Reserved



